Allison Transmission Wont Shift into Gear: Expert Guide & Solutions
When an Allison transmission won’t shift into gear, it’s often due to issues such as low or degraded transmission fluid, malfunctioning shift…
When an Allison transmission won’t shift into gear, it’s often due to issues such as low or degraded transmission fluid, malfunctioning shift solenoids, a damaged valve body, or electronic control module malfunctions. Addressing these concerns promptly and ensuring regular maintenance can restore your transmission’s performance.
In the vast realm of automotive engineering, Allison Transmission stands as a beacon of reliability and performance. For over a century, this brand has been synonymous with top-tier transmission systems, ensuring vehicles run smoothly and efficiently.
However, like any mechanical component, issues can arise. One of the most perplexing challenges drivers face is when the Allison Transmission won’t shift into gear. Let’s delve into this issue, understand its symptoms, causes, and chart a course for resolution.
Highlighting the Main Issue
However, even the most robust systems are not devoid of challenges. Imagine cruising down the highway, the horizon beckoning, when suddenly your vehicle refuses to shift gears. Or picture a busy morning, running late for a meeting, and your car remains stagnant, despite the engine roaring to life.
These are real-world scenarios many drivers have grappled with, facing the perplexing issue of an Allison Transmission that won’t shift into gear.
Such situations are not just frustrating; they pose potential risks. Being stranded in the middle of a journey, especially in adverse conditions, can be hazardous. Moreover, a malfunctioning transmission can lead to further mechanical issues, escalating repair costs and jeopardizing the vehicle’s longevity.
- You Can See: How to Manually Shift Allison Transmission
Common Causes and Solutions
Fluid Level and Quality Issues

The lifeblood of any transmission system, especially the Allison Transmission, is its fluid. This isn’t just a lubricant—it’s a multi-functional component that facilitates gear shifts, cools the transmission, and cleans internal parts.
The Role of Transmission Fluid:

Lubrication: Reduces friction between moving parts, preventing wear and tear.
Cooling: Helps dissipate heat generated during gear shifts, ensuring the transmission doesn’t overheat.
Cleaning: Modern transmission fluids contain detergents that help keep the internals clean.
Hydraulic Function: Assists in the hydraulic operations of the transmission, enabling smooth gear shifts.
Potential Issues:
Low Fluid Levels: This can lead to overheating, delayed shifting, or no shifting. It’s often a sign of leaks in the system.
Degraded Fluid: Over time, the fluid can degrade, losing its essential properties. This can lead to sluggish shifts, noises, or even transmission failure.
Solution:
Regular Checks: At least once a month, check the fluid level and its condition. Use the dipstick to ensure it’s within the recommended range and observe its color. Healthy fluid is usually a clear red. If it’s brownish or has a burnt smell, it’s time for a change.
Fluid Replacement: Depending on the vehicle’s usage, consider changing the transmission fluid every 30,000 to 60,000 miles.
- You Can See: How to Check Transmission Fluid on 2007 Dodge Charger
- Product Recommendation: Best Transmission Fluid for Allison Transmissions
Faulty Shift Solenoids
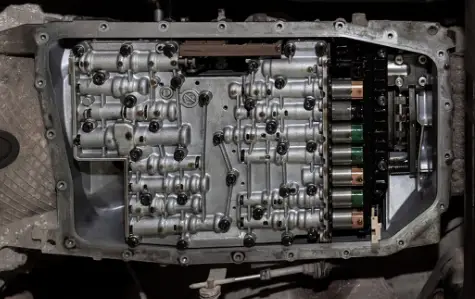
Shift solenoids are electro-hydraulic valves that control the flow of transmission fluid around the gearbox, determining when and how gears shift.
How They Work:
The ECM sends electrical signals to the solenoids based on various factors like engine speed, vehicle speed, and the position of the throttle.
These signals either open or close the solenoids, directing the transmission fluid to specific pathways, resulting in gear shifts.
Potential Issues:
Stuck or Malfunctioning Solenoids: This can lead to hard or soft shifts, delayed shifts, or the transmission getting stuck in a specific gear.
Electrical Issues: Wiring problems or ECM malfunctions can disrupt the signals to the solenoids.
Solution:
Diagnostic Test: Use a multimeter or a diagnostic tool to check the solenoid’s resistance. If it’s outside the manufacturer’s specifications, replacement is necessary.
Visual Inspection: Check for damaged wiring or connections. Ensure the solenoids are clean and free from debris.
Diagnosing Shift Solenoid Issues
Damaged Valve Body
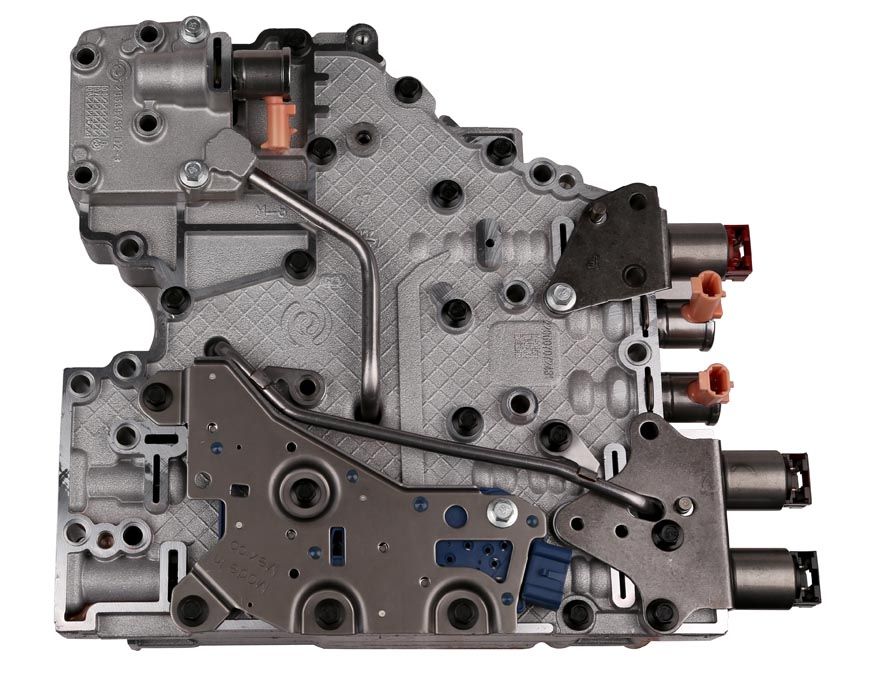
The valve body is a maze of channels and valves that direct fluid to various clutches and bands, determining which gear the vehicle should be in.
How It Operates:
As you accelerate or decelerate, the transmission fluid is directed through different channels in the valve body.
This fluid movement activates specific gears, ensuring optimal vehicle performance.
Potential Issues:
Blocked Channels: Debris or degraded transmission fluid can block channels, disrupting fluid flow.
Worn-Out Valves: Over time, the valves in the body can wear out, leading to leaks or improper fluid direction.
Solution:
Regular Cleaning: Ensure the valve body is cleaned during transmission fluid changes to prevent blockages.
Replacement or Repair: If there’s significant wear or damage, consider replacing or repairing the valve body.
- You Can See: Subaru Transmission Valve Body Replacement Cost
Electronic Control Module Malfunctions
The ECM is the brain behind the transmission, ensuring seamless communication between the engine, transmission, and other vital systems.
Its Role:
It gathers data from various sensors, like speed sensors and throttle position sensors.
Based on this data, it determines the best time and way to shift gears.
Potential Issues:
Faulty Sensors: If a sensor provides incorrect data, the ECM might make wrong shifting decisions.
Software Glitches: Outdated or corrupted software can lead to erratic transmission behavior.
Solution:
Error Code Reading: Use a diagnostic tool to read error codes. This can pinpoint the exact issue, whether it’s a faulty sensor or a software problem.
ECM Reset or Update: Sometimes, simply resetting the ECM or updating its software can resolve issues.
Symptoms of Allison Transmission Not Shifting
No Forward or Reverse Movement
When the Allison Transmission refuses to engage in either forward or reverse gear, it’s as if the vehicle is in a perpetual state of neutral. The engine might rev, but there’s a disconcerting lack of movement, leaving the vehicle stationary.
Immediate Steps:
Ensure your safety first. If you’re on the road, turn on your hazard lights and try to move your vehicle to a safe location.
Check the transmission fluid level. A significant drop could be the culprit.
Avoid excessive revving, as this can exacerbate the issue.
Seek professional assistance. It’s advisable not to drive the vehicle until the issue is diagnosed and resolved.
Unusual Noises When Trying to Shift
A healthy transmission operates with seamless harmony, but when issues arise, this harmony is disrupted, often audibly. Noises like grinding indicate gear synchronization problems, while a whining sound might point to low fluid levels or pump issues.
Sounds like a failing transmission
Delayed or Rough Shifting
Instead of the usual swift and smooth transition between gears, there’s a noticeable hesitation. This delay can feel like a momentary lapse where the vehicle seems unresponsive. It’s often accompanied by a jolt or jerk when the gear finally engages.
Potential causes range from degraded transmission fluid, and malfunctioning shift solenoids, to more severe internal damages.
Dangers:
Reduced vehicular control, especially during crucial maneuvers.
Increased wear and tear on the transmission, potentially leading to more severe issues.
Elevated risk of accidents, especially if the vehicle jerks unpredictably in traffic.
Deep Dive into Topics
Understanding the Allison Transmission Mechanism
Allison Transmissions, renowned for their durability and efficiency, are intricate systems that require a symphony of components to work in harmony. Let’s delve deeper into its mechanism:
Torque Converter:
This is the connection between the engine and the transmission. It uses transmission fluid to transfer power from the engine to the transmission, allowing for smooth acceleration from a stop.
Potential Issues: Wear and tear can lead to a malfunctioning converter, causing slippage or overheating.
Solution: Regular inspections and ensuring the use of quality transmission fluid can prolong the converter’s life.
Planetary Gear Sets:
These are the heart of the transmission, allowing for various gear ratios. They consist of sun gear, planet gear, and ring gear.
Potential Issues: Worn-out gears can lead to noisy operation and inefficient gear shifts.
Solution: Regular maintenance checks and addressing issues promptly can prevent severe damage.
Clutches and Bands:
These components lock and release different parts of the gear sets to achieve the desired gear ratio.
Potential Issues: Worn-out clutches or bands can lead to slippage or the transmission getting stuck in a particular gear.
Solution: Periodic inspections and replacements when signs of wear are evident.
Hydraulic System:
This system uses transmission fluid to operate the clutches and bands based on the signals from the valve body.
Potential Issues: Leaks or blockages can disrupt the hydraulic pressure, affecting gear shifts.
Solution: Regular fluid checks and ensuring the valve body is free from debris can maintain optimal hydraulic function.
[Prompt for Image: Diagram of Allison Transmission components]
Step-by-Step Diagnostic Guide
Facing issues with your Allison Transmission? Before heading to a mechanic, here’s a step-by-step guide to diagnosing potential problems:
Visual Inspection: Begin by checking for any visible leaks under the vehicle. Transmission fluid is typically red or brown.
Check Fluid Levels and Quality: Using the dipstick, ensure the fluid is within the recommended range and observe its color and smell. Dark or burnt-smelling fluid indicates a problem.
Listen for Noises: Start the vehicle and listen for any unusual sounds like whining or grinding. These could indicate internal damage.
Check for Error Codes: If you have a diagnostic tool, scan for any transmission-related error codes. This can provide insights into potential issues.
Shift Through Gears: With the vehicle stationary, shift through all gears and observe any delays or rough shifts.
Test Drive: If safe, take the vehicle for a short drive, paying attention to gear shifts, noises, and any vibrations.
DIY Allison Transmission Diagnosis
Maintenance Tips to Prevent Shifting Issues
To ensure your Allison Transmission operates smoothly for years:
Regular Fluid Changes: Depending on your driving conditions, change the transmission fluid every 30,000 to 60,000 miles.
Avoid Overloading: Consistently overloading your vehicle can strain the transmission.
Warm-Up: Especially in colder climates, allow your vehicle to warm up before driving.
Regular Inspections: Periodically inspect the transmission for leaks, wear, or any unusual signs.
Stay Updated: Ensure the transmission’s software is up-to-date, especially in newer models with advanced electronic systems.
- Product Recommendation: Maintenance Kit for Allison Transmissions

FAQs
Why is my Allison transmission not going into gear?
There could be several reasons for this issue. Common culprits include low or degraded transmission fluid, malfunctioning shift solenoids, a damaged valve body, or issues with the electronic control module (ECM). It’s essential to diagnose the exact cause to address it effectively.
What does it mean when there’s no forward or reverse movement in an Allison transmission?
This typically indicates a severe transmission issue. The problem could stem from low transmission fluid, a faulty torque converter, or issues within the valve body. Immediate professional attention is recommended to prevent further damage.
How do I identify a faulty shift solenoid in an Allison transmission?
Symptoms of a faulty shift solenoid include erratic shifting patterns, delayed shifts, or the transmission getting stuck in a particular gear. A diagnostic tool can help identify solenoid issues by reading error codes related to the transmission.
Is it expensive to fix an Allison transmission that won’t shift?
The cost of repairs can vary based on the underlying issue. For instance, replacing the transmission fluid or a shift solenoid is relatively inexpensive. However, repairing or replacing the valve body or the entire transmission can be more costly. It’s always best to diagnose the problem early to prevent more expensive repairs down the line.
How often should I change the transmission fluid in my Allison transmission?
As a general guideline, consider changing the transmission fluid every 30,000 to 60,000 miles. However, this can vary based on driving conditions, the type of fluid used, and the specific model of the Allison transmission. Always refer to the vehicle’s owner manual for specific recommendations.
Can software issues affect my Allison transmission’s shifting?
Yes, modern Allison transmissions rely on electronic systems and software to optimize gear shifts. Outdated or corrupted software can lead to shifting issues. Regular updates and ensuring the electronic control module (ECM) functions correctly can prevent such problems.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of automotive issues, especially when it pertains to a system as integral as the transmission, can be daunting. Allison Transmission, with its storied legacy and engineering prowess, stands as a testament to automotive excellence.
Yet, like all mechanical marvels, it isn’t immune to challenges. The inability to shift into gear, while concerning, is a problem with solutions at hand.
Understanding the symptoms is the first step toward resolution. Whether it’s the unsettling stillness of no movement or the audible alarms of grinding and whining, recognizing these signs early can prevent further complications.
Coupled with immediate actions and professional intervention, these issues can be addressed, ensuring the longevity and performance of your Allison Transmission.
See Also:







