How Much Does a Transmission Cost? (2024 Price Guide)
📌 Quick Summary A transmission replacement typically costs $2,500 to $5,000 including parts and labor, though high-end luxury vehicles or CVTs can…
A transmission replacement typically costs $2,500 to $5,000 including parts and labor, though high-end luxury vehicles or CVTs can exceed $6,000. The total price depends heavily on whether you choose a used, rebuilt, or remanufactured unit.
🎯 Key Takeaways
- Takeaway 1:Remanufactured transmissions offer the best balance of reliability and long-term cost.
- Takeaway 2:Labor usually accounts for $500 to $1,500 of the total replacement cost.
- Takeaway 3:AWD and 4WD vehicles increase labor time and overall transmission pricing significantly.
- Takeaway 4:CVT transmissions are often more expensive to replace than traditional automatic systems.
- Takeaway 5:Get at least three quotes to compare shop labor rates and warranty terms.
Replacing a transmission is one of the most expensive repairs you will ever face as a vehicle owner. On average, you should expect to pay between $2,800 and $6,500 for a total replacement, though luxury models or heavy-duty trucks can easily push those figures over $8,000. The final price you see on your invoice depends heavily on whether you choose a used, rebuilt, or remanufactured unit, as well as the complexity of your vehicle’s drivetrain.

Understanding these costs is critical because the price difference between a quick fix and a long-term solution can be thousands of dollars. Whether your gears are slipping or your car won’t move at all, your goal is to find the best balance between reliability and your budget. This guide breaks down the actual numbers you will encounter at the shop so you can make an informed decision without the guesswork.
Breakdown of Transmission Replacement Costs: Used vs. Rebuilt vs. Remanufactured
The biggest variable in your total out-of-pocket cost is the type of transmission being installed. You aren’t just paying for a hunk of metal; you are paying for the peace of mind and the lifespan of the unit. Each of the following options comes with a different price point and level of risk.

Comparing the Four Main Replacement Options
Most shops will offer you three or four distinct paths for getting your car back on the road. Here is how the total costs (parts and labor) typically stack up in 2024:
- Used Transmission ($1,200 – $2,500): These are sourced from salvage yards or “donor” vehicles. While they are the cheapest option, they usually come with a limited 30-to-90-day warranty and unknown internal wear.
- Rebuilt Transmission ($3,000 – $5,000): Your existing transmission is disassembled and inspected by a local technician. Worn parts are replaced, and the unit is put back together. This is a common mid-range solution for older vehicles.
- Remanufactured Transmission ($3,500 – $6,500): These units are sent to a factory and restored to “as-new” specifications. All internal components are replaced, and any known factory defects are corrected. This usually includes the best warranty (often 3 years/100,000 miles).
- New Transmission ($4,500 – $9,000+): Sourced directly from the manufacturer (OEM), these are rare because the cost often exceeds the value of the car. These are typically only found in brand-new vehicles under warranty or high-end exotic cars.
Which Option Should You Choose?
If you plan on keeping your car for more than two years, a remanufactured unit is often the best value. Although the upfront cost is about 20% higher than a rebuild, the extended warranty covers both the part and the labor at most shops across the country. Conversely, if you are simply trying to get a high-mileage vehicle running so you can consumer.ftc.gov/articles/auto-repair-basics” target=”_blank” rel=”noopener noreferrer” title=”Federal Trade Commission guide to auto repair costs”>trade
it in, a used transmission is the most budget-friendly way to restore functionality.Everything You Need to Know About Transmission Costs
Determining the cost of a transmission repair or replacement is one of the most stressful experiences a vehicle owner can face. Because transmissions are the most complex mechanical components in modern cars, prices can fluctuate by thousands of dollars based on your vehicle’s make, the severity of the damage, and the labor rates in your specific region. This guide provides a comprehensive, step-by-step roadmap to help you navigate the diagnostic process, evaluate your repair options, and accurately estimate the total financial impact on your wallet. By following these steps, you can avoid overpaying and ensure your vehicle receives the right level of service.
Step 1: Identify Your Specific Vehicle and Transmission Profile
What you need: Your Vehicle Identification Number (VIN), owner’s manual, and a smartphone or computer for research.
Instructions: Transmission costs are highly sensitive to the specific model of the gearbox installed in your car. A standard front-wheel-drive (FWD) four-speed automatic from 2005 will cost significantly less than a modern 10-speed dual-clutch transmission (DCT) or a Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT). Locate your VIN on the driver’s side dashboard or door jamb. Use an online VIN decoder to identify the exact transmission model (e.g., a ZF 8HP70 or a Ford 10R80). Note whether your vehicle is FWD, Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD), or All-Wheel Drive (AWD), as AWD systems often require extra labor to remove transfer cases, adding $300 to $600 to the total labor bill.
Pro Tip: Look for a white sticker on the driver’s side door pillar; it often contains a “TR” code which specifies the transmission family, helping you get more accurate quotes from shops.
Step 2: Perform a Preliminary Diagnostic Assessment
What you need: An OBD-II code scanner, a clean rag, and a flashlight.
Instructions: Before assuming you need a multi-thousand dollar replacement, check the transmission fluid level and color. Bright red fluid is healthy; dark, burnt-smelling fluid indicates internal friction and damage. Use an OBD-II scanner to pull “P” codes (Powertrain codes). Codes like P0700 are general, but specific solenoid codes might indicate that a $200 electronic repair is all you need. If the car is “slipping” (engine revs but the car doesn’t move proportionately), the internal clutches are likely worn out. Document these symptoms carefully to present to a mechanic, as being specific can prevent them from recommending a full replacement for a minor sensor issue.
Pro Tip: Never clear the codes before taking the car to a professional; the “freeze frame” data associated with the code tells the mechanic exactly what the car was doing when it failed.
Step 3: Choose Between Repair, Rebuild, or Replace
What you need: A notebook to compare price quotes and a clear understanding of your long-term plans for the vehicle.
Instructions: You have three financial paths. A “Repair” involves fixing a specific part (like a torque converter or valve body) and costs $500–$1,500. A “Rebuild” involves taking your existing transmission apart, cleaning it, and replacing worn components; this typically costs $2,500–$4,500 and is labor-intensive. A “Replacement” involves installing a different unit. This could be a “Remanufactured” unit (factory-refurbished to original specs) costing $3,500–$6,000, or a “Used” unit from a salvage yard costing $800–$2,000 plus labor. If you plan to keep the car for five more years, a remanufactured unit with a long warranty is the best value despite the higher upfront cost.
Pro Tip: Be wary of “soft” rebuilds where shops only replace the seals and gaskets; ensure they are also replacing the clutches and bands for a true “hard” rebuild.
Step 4: Source and Compare Part Prices
What you need: Access to online wholesale parts databases and phone numbers for local salvage yards.
Instructions: If you are buying a replacement unit yourself to save money, compare different sources. Remanufactured units from national suppliers (like Jasper or Street Smart) often come with a 3-year, 100,000-mile nationwide warranty, which includes labor if the unit fails. These usually cost between $2,800 and $4,500 for most passenger vehicles. If you choose a used transmission, check the mileage of the donor vehicle and ensure the yard offers at least a 90-day exchange warranty. Used units for common cars like a Honda Accord might be as low as $600, while a used unit for a heavy-duty diesel truck could still cost $2,500.
Pro Tip: When buying a used transmission, ask for the VIN of the donor car so you can verify the mileage independently through a vehicle history report.
Step 5: Calculate Estimated Labor Costs
What you need: Local labor rates (hourly) and a labor time guide (like AllData or Mitchell 1).
Instructions: Labor is often the most variable part of the cost. Most transmission swaps take between 8 and 15 hours of labor. In rural areas, shop rates might be $90 per hour, while in major cities or at dealerships, rates can exceed $180 per hour. For a standard RWD truck, expect 6–8 hours ($720–$1,440). For a complex European AWD SUV, expect 12–20 hours ($1,440–$3,600). Always ask the shop if their quote is a “flat rate” or based on “actual hours.” Flat rates are safer for the consumer as they protect you if the mechanic runs into rusty bolts or complications that slow down the process.
Pro Tip: Dealerships usually have the highest labor rates but the best specialized tools; independent transmission specialty shops often provide the best balance of expertise and price.
Step 6: Account for Fluids, Filters, and Ancillary Parts
What you need: A list of manufacturer-approved transmission fluids and a quote for a new transmission cooler.
Instructions: Don’t forget the “hidden” costs. A full transmission replacement requires fresh fluid, which can be expensive. Many modern transmissions use synthetic fluids costing $15–$30 per quart, and you may need 10–12 quarts ($150–$360). Additionally, if your old transmission suffered a mechanical failure, metal shavings are likely trapped in your transmission cooler and lines. You must either spend $150–$250 on a professional “hot flush” of the cooling system or $200–$400 to replace the cooler entirely. Failing to do this will cause the debris from the old transmission to ruin the new one within weeks, often voiding your warranty.
Pro Tip: Always insist on OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) fluid rather than “universal” brands, as many transmissions have specific friction modifiers required for smooth shifting.
Step 7: Verify Warranty Coverage and Final Quotes
What you need: Written estimates from at least three different shops and a highlighter.
Instructions: Collect detailed written quotes that break down parts, labor, fluid, and disposal fees. Compare the warranties side-by-side. A “local” warranty is only good at that specific shop, which is a problem if you move or break down on a road trip. A “nationwide” warranty is far superior. Check if the warranty covers “parts and labor” or just “parts.” If a $3,000 transmission fails under a “parts only” warranty, you will still have to pay $1,500 in labor to have it swapped again. Verify the “core charge” as well—this is a deposit (usually $500–$1,000) you pay upfront and get back once your old transmission is returned to the manufacturer.
Pro Tip: Check the shop’s reputation on the Better Business Bureau or Google Reviews specifically looking for how they handle warranty claims when things go wrong.
✅ Final Checklist
- Verified the exact transmission model via VIN to ensure part compatibility.
- Obtained an OBD-II diagnostic report to rule out simple sensor or solenoid failures.
- Decided between used ($800+), rebuilt ($2,500+), or remanufactured ($3,500+).
- Confirmed the labor hour estimate (usually 8-15 hours) and hourly rate.
- Ensured the quote includes a cooling system flush and 10+ quarts of OEM fluid.
- Confirmed the warranty terms (Length, Mileage, and Nationwide coverage).
Important Notes:
- Safety First: Never crawl under a vehicle supported only by a bumper jack; always use rated jack stands on a level surface if inspecting fluid or codes yourself.
- Seek Professional Help: If your car has a complex hybrid system or a dual-clutch transmission, these often require specialized computer “re-learning” procedures that only a high-end shop can perform.
- Estimated Time: Diagnostic (1-2 hours); Repair/Replacement (2-5 business days).
- Cost Range: Total costs typically range from $2,500 to $6,000 for most modern vehicles.
Labor Hour Estimates and Average Shop Rates for Transmission Work
The transmission is the most labor-intensive component of your vehicle. It is buried deep within the engine bay or tucked under the chassis, requiring the removal of dozens of peripheral components just to access it. When you look at your estimate, the labor cost will often represent 30% to 50% of the total bill.
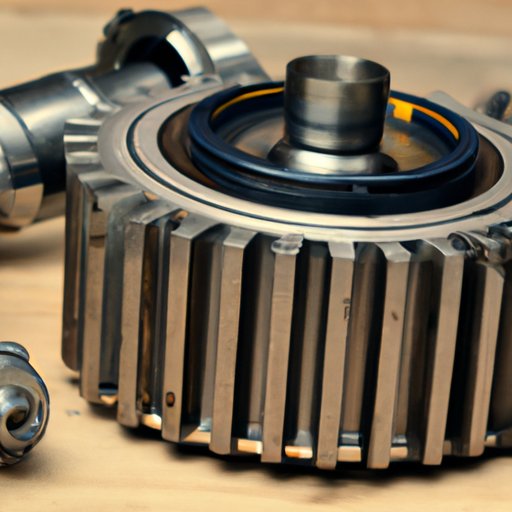

Average Labor Hours by Vehicle Type
The time it takes to “R&R” (remove and replace) a transmission varies significantly based on your car’s layout. On average, expect the job to take 8 to 15 hours of specialized labor. Here is a breakdown of how different vehicle types affect that timeline:
- Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD) Trucks/SUVs: 5 to 8 hours. These are generally the easiest to service because the transmission is easily accessible underneath the vehicle.
- Front-Wheel Drive (FWD) Sedans: 8 to 12 hours. Because the engine and transmission (transaxle) are packed tightly in the front, mechanics often have to drop the entire subframe to get the unit out.
- All-Wheel Drive (AWD) and 4WD Vehicles: 12 to 16+ hours. These systems require the technician to disconnect transfer cases and additional driveshafts, significantly increasing the complexity and the clock time.
Hourly Rates and Shop Selection
Where you take your vehicle is just as important as what vehicle you drive. Labor rates are not standardized and will fluctuate based on your geographic location and the type of facility you choose.
- Independent Repair Shops: $110 – $150 per hour. These shops offer the most competitive pricing and are often more willing to install used or aftermarket parts to save you money.
- Transmission Specialty Shops (e.g., AAMCO): $130 – $180 per hour. Because they focus exclusively on drivetrains, they may work faster, but their specialized expertise comes at a premium.
- Dealership Service Centers: $180 – $250+ per hour. Dealers have the highest overhead and strictly use OEM parts. You will get factory-trained technicians, but you will pay the highest possible price for that expertise.
For a standard 10-hour job at an average rate of $140 per hour, you are looking at $1,400 in labor alone, before a single part or a quart of transmission fluid is even billed to your account. This is why getting multiple quotes is essential; a $30 difference in hourly rates can save you $300 to $500 on the final invoice.
Factors That Influence the Final Price: CVTs, Luxury Brands, and Drivetrains
Not all transmissions are created equal, and the specific technology under your hood is the biggest variable in your final bill. While a standard automatic for a domestic sedan might be relatively affordable, specialized systems can send quotes into the stratosphere. Understanding what you are driving is the first step in estimating your potential financial hit.
The CVT Premium and Specialized Components
Many modern vehicles, especially those from brands like Nissan, Honda, and Toyota, utilize Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVTs). While these offer great fuel efficiency, they are notoriously expensive to fix. Unlike traditional automatics, CVTs are often treated as “sealed units,” meaning mechanics frequently replace the entire unit rather than repairing individual internal parts. A CVT replacement can easily cost between $3,000 and $5,500.
Drivetrain Complexity and Brand Tax
Your vehicle’s drivetrain layout significantly impacts labor hours. For example, a Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD) truck usually offers easier access to the transmission than a cramped Front-Wheel Drive (FWD) compact car. However, All-Wheel Drive (AWD) and 4WD vehicles are the most expensive because the transmission is connected to transfer cases and additional driveshafts that must be disassembled.
- Luxury Brands: If you drive a BMW, Mercedes-Benz, or Audi, expect to pay a “luxury tax.” Parts are often imported, and specialized software is required to “flash” the new transmission to the car’s computer.
- Heavy-Duty Trucks: Transmissions for towing (like the Allison units in Chevy Duramax trucks) are built to handle massive torque and come with a price tag to match, often exceeding $6,000.
- Labor Rates: Dealerships typically charge $150–$250 per hour, while independent shops may range from $90–$150.
Cost Comparison: Transmission Repair vs. Full Replacement
When your mechanic delivers the bad news, you usually have a choice: repair the specific problem or swap the whole unit. Deciding between a “band-aid” fix and a total overhaul depends on the age of your vehicle and the extent of the internal damage. Sometimes, spending more upfront on a replacement saves you from a second breakdown six months later.
When a Minor Repair Makes Sense
If your car is shifting poorly but the internal gears are still healthy, you might get away with a minor repair. Common “external” fixes include replacing a shift solenoid, a leaking output shaft seal, or a faulty speed sensor. These repairs usually range from $300 to $800. If the fluid is clean and there are no metal shavings in the pan, a repair is almost always the smarter financial move.
The Tipping Point for a Full Replacement
Once a transmission has “slipped” significantly, the internal clutches are likely burnt. In this case, a simple repair won’t suffice. You then have three main options for replacement:
- Used Transmission ($800 – $2,000): The cheapest route, sourced from a salvage yard. It’s a gamble, as you don’t know the part’s history, but it’s great for older cars.
- Rebuilt Transmission ($2,500 – $4,500): Your existing transmission is taken apart and worn pieces are replaced. This is a solid middle-ground option.
- Remanufactured Transmission ($3,500 – $6,000): These are processed in a factory to original equipment manufacturer (OEM) specs. They usually come with the best warranties (3 years/100,000 miles).
Pro Tip: Always check if your vehicle is under a Powertrain Warranty. Many manufacturers cover the transmission for up to 60,000 or even 100,000 miles, which could bring your out-of-pocket cost down to zero.
Conclusion
Navigating transmission costs in 2024 can be daunting, with average prices ranging from $2,500 to over $5,000 depending on your vehicle type and the severity of the damage. While luxury brands and complex CVTs push prices higher, catching problems early through routine fluid checks can often save you from a total replacement. Remember to weigh the value of your car against the cost of the repair—sometimes a remanufactured unit with a long warranty is the best way to protect your investment.
Next Steps: If you suspect your transmission is failing, start by checking your fluid levels and getting a diagnostic scan at a local shop. Don’t wait until the car stops moving entirely! Compare at least two quotes from reputable local transmission specialists to ensure you’re getting a fair price for your 2024 repair.
💬 Quick Questions & Answers
What is the average cost of a rebuilt transmission?
A rebuilt transmission typically costs between $2,500 and $4,500 including labor.
How many hours of labor does it take to replace a transmission?
Most shops estimate between 8 and 15 hours depending on vehicle complexity.
Is it cheaper to fix or replace a transmission?
Minor repairs cost $300-$800, but major internal damage usually warrants a full replacement.
Do luxury cars cost more for transmission work?
Yes, parts for BMW, Mercedes, or Audi can double the standard replacement price.
How much does a used transmission cost?
A used unit typically costs $800 to $1,500 for the part alone.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference in cost between a remanufactured and a rebuilt transmission?
A remanufactured unit is factory-corrected and costs $2,500-$4,000, while a rebuild is done locally for $2,000-$3,500. Remanufactured units generally come with better nationwide warranties.
Why are CVT transmissions more expensive to replace?
CVTs are complex, often non-serviceable, and usually require a full unit replacement rather than a repair. This pushes costs toward the $4,000-$6,000 range.
Does car insurance cover transmission failure?
Standard insurance only covers transmission damage resulting from an accident, not mechanical failure or wear. Mechanical breakdown insurance or an extended warranty is required for non-accident coverage.
How much extra does AWD or 4WD add to the cost?
These systems require removing more components like transfer cases and extra driveshafts, adding 2-4 hours of labor. This typically increases the total bill by $400 to $800.
Is it worth replacing a transmission on a high-mileage car?
If the cost exceeds 50% of the vehicle’s total value, it may be better to trade it in. Always consider the overall mechanical health before investing $4,000 or more.
What is a typical shop labor rate for transmission work?
Independent shops usually charge between $90 and $150 per hour, while dealerships often charge $160 to $250 per hour for specialized transmission technicians.